In the world of infrastructure maintenance, the hidden heroes often remain unnoticed. Yet, they play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of our cities and towns. Among these unsung heroes are pipe relining techniques, a method employed to rehabilitate aging or damaged pipelines without the need for extensive excavation. While it may not be as glamorous as constructing towering skyscrapers or sleek bridges, sewer relining holds significant importance in ensuring the longevity and efficiency of our underground utilities.
The Need for Pipe Relining
As urban landscapes continue to evolve and expand, so does the demand on infrastructure, including water and sewer systems. Many of these systems were constructed decades ago, using materials such as cast iron, clay, or concrete. Over time, these materials deteriorate due to various factors like corrosion, ground movement, and tree root intrusion, leading to leaks, blockages, and structural weaknesses.
Traditionally, the solution to such problems involved excavating the affected pipe section and replacing it with a new one. However, this process is not only disruptive but also expensive, time-consuming, and often requires the destruction of surrounding infrastructure like roads and sidewalks. This is where pipe relining techniques come into play, offering a more cost-effective and efficient alternative.
Understanding Pipe Relining
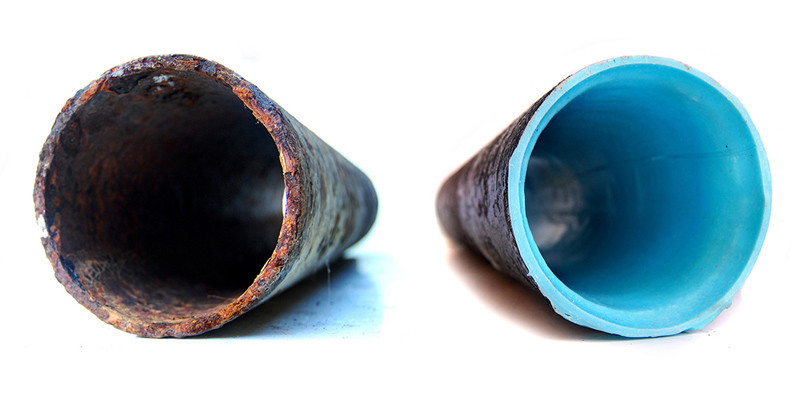
Pipe relining, also known as cured-in-place pipe (CIPP) rehabilitation, involves inserting a resin-saturated liner into the existing pipe. Once in place, the liner is inflated and cured, creating a seamless, durable, and corrosion-resistant barrier within the old pipe. This process effectively restores the structural integrity of the pipeline, seals any existing leaks, and prevents future deterioration.
One of the key advantages of pipe relining is its versatility. It can be applied to pipes of various shapes, sizes, and materials, including PVC, concrete, clay, and even asbestos. Whether it’s a small residential sewer line or a large municipal water main, pipe relining offers a viable solution for rehabilitation without the need for extensive excavation.
Cost-Effectiveness of Pipe Relining
When comparing the cost of traditional pipe replacement with pipe relining, the difference is often significant. Here’s why:
- Reduced Labor and Equipment Costs: Excavation and replacement require heavy machinery, skilled labor, and substantial manpower. In contrast, pipe relining involves minimal excavation, reducing labor hours and equipment expenses.
- Minimal Disruption: Traditional pipe replacement can disrupt traffic flow, disrupt businesses, and inconvenience residents. Pipe relining minimizes disruption since it requires less excavation and can often be completed without digging up entire sections of road or sidewalk.
- Faster Completion Time: Pipe relining typically takes less time to complete compared to traditional replacement methods. This means less downtime for utilities and reduced inconvenience for the community.
- Long-Term Savings: While the initial cost of pipe relining may be higher than simple patching or spot repairs, its longevity and durability result in long-term savings. A properly relined pipe can last several decades, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacements.
Environmental Benefits
Beyond its cost-effectiveness, pipe relining also offers environmental benefits. By minimizing excavation and reducing the need for new pipe materials, it helps conserve natural resources and reduces carbon emissions associated with construction activities. Additionally, since it prevents leaks and reduces the risk of contamination, it helps protect water quality and ecosystem health.
Conclusion
Pipe relining techniques represent a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution to the challenges posed by aging or damaged pipelines. By offering a viable alternative to traditional excavation and replacement methods, they help extend the lifespan of underground utilities while minimizing disruption to communities and reducing long-term maintenance costs.